by Cody Dumont
November 30, 2016
Many organizations deploy patch management solutions that can be complex and difficult to manage effectively. Although, these solutions provide the ability to manage clients, deploy software applications, and perform routine patching, additional problems and increase risks can arise for the organization if left unmanaged. This dashboard provides a high-level overview of vulnerabilities reported by Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM), which can help to determine whether vulnerabilities are being patched effectively.
SCCM provides organizations with the ability to deploy operating systems, manage client health, push software patches, and the ability to quickly rebuild systems. Although SCCM can provide an effective patch management solution, organizations must have a strategy in place to assess existing risks, while patching systems in a timely manner. Organizations must also address stand-alone systems or hosts isolated from the main network that may not be a part of an enterprise-wide patch management solution. These systems not managed with SCCM can be easily overlooked by administrators, as scanning and patching these systems manually can leave potentially critical systems and data vulnerable to attack. By continuously testing, monitoring, and rescanning all systems to ensure patches have been applied correctly, organizations can help to keep Windows-based systems secure and up to date.
The SCCM Patch Management Overview dashboard provides a comprehensive look at Microsoft vulnerabilities detected by SCCM, as well as other patch management solutions and stand-alone systems. Components within this dashboard can be useful in comparing the effectiveness of existing SCCM patch management efforts and whether existing security controls need to be modified. Analysts can use this information to focus efforts on identifying both current and previously mitigated vulnerabilities. Using the results from active Tenable Nessus scans, analysts can easily compare vulnerability results against those reported by SCCM. This comparison of information can be useful in detecting hosts reporting potentially outdated or inaccurate data.
Vulnerabilities detected by Nessus can be used to detect stand-alone systems not managed by SCCM, and aid in comparing the efficacy of patch management efforts. Events reported by SCCM can alert analysts to package deployments and service-related issues that should be reviewed further. Information on SCCM client systems can help analysts detect hosts that may not be reporting properly, or that are not managed by SCCM. Organizations can use this dashboard to proactively address and strengthen overall network security and patch management efforts across the network.
This dashboard is available in the Security Center Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, Assurance Report Cards, and assets. The dashboard can be easily located in the Security Center Feed under the category Discovery & Detection. The dashboard requirements are:
- Security Center 5.4.0
- Nessus 8.5.1
Tenable transforms security technology for the business needs of tomorrow through comprehensive solutions that provide continuous visibility and critical context, enabling decisive actions to protect the organization. Tenable Security Center is continuously updated with information about advanced threats and zero-day vulnerabilities, and new types of regulatory compliance configuration audit files. Active scanning examines running systems and services, detects vulnerable software applications, and analyzes configuration settings. Passive listening collects data to continuously monitor traffic, collect information about user privilege changes, and administrative activity, along with the discovery of additional vulnerabilities. Host data and data from other security products is analyzed to monitor patch management solutions on the network. Monitoring the network to ensure that all systems are secured against vulnerabilities is essential to ongoing security efforts. Tenable enables powerful, yet non-disruptive, continuous monitoring that will enable organizations with the information needed to proactively respond to threats within the enterprise.
The following components are included within this dashboard:
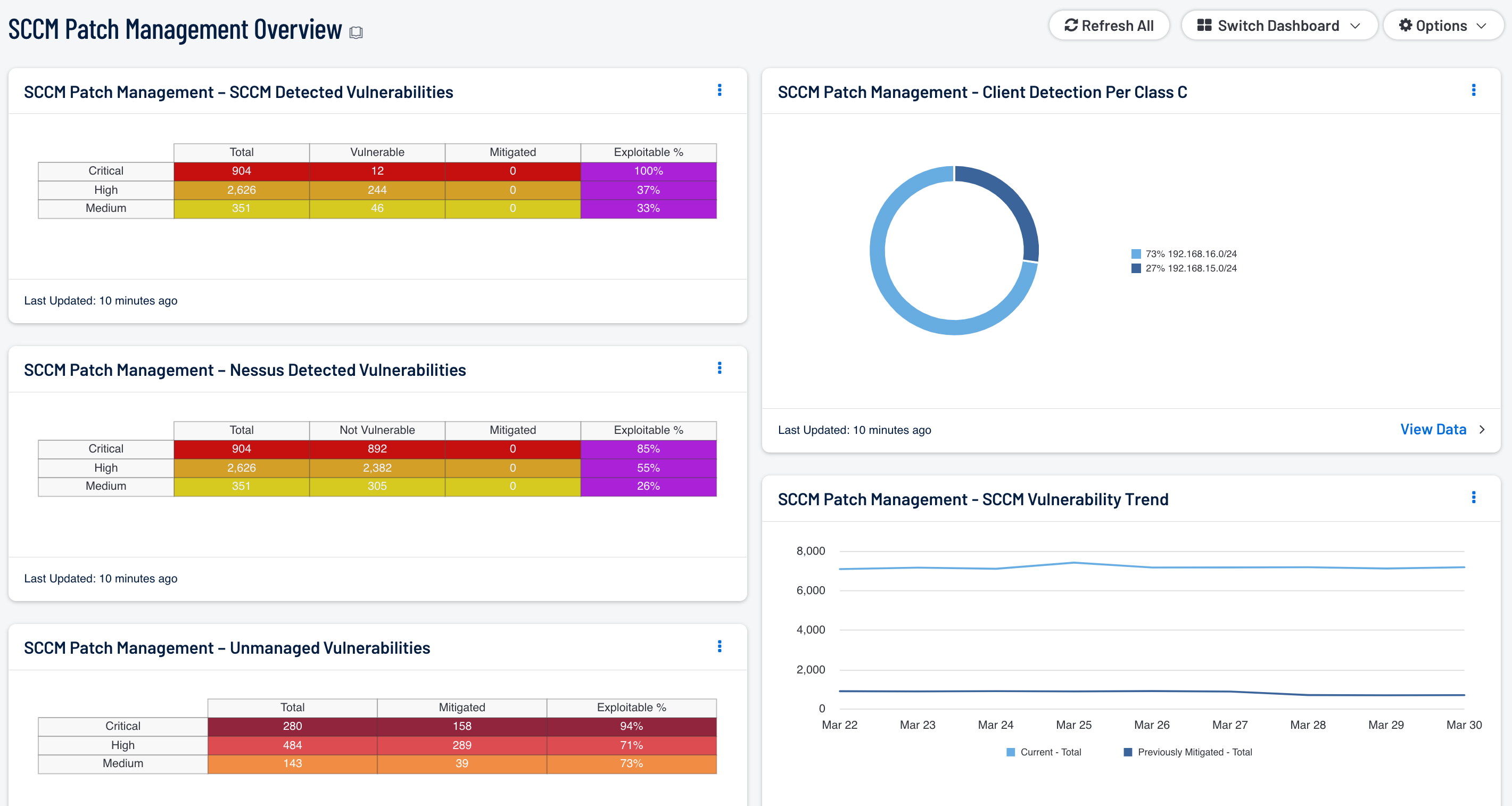
- SCCM Patch Management - SCCM Vulnerability Trend: This component presents a trend line chart of both current and previously mitigated vulnerabilities reported by SCCM over the last seven days. Information presented within this component can provide organizations with a comprehensive view into how often systems are being scanned, patched, and rescanned. Current vulnerabilities are identified and set to the “Never Mitigated” filter. When a vulnerability moves from the mitigated section to the active section, the mitigation status is set to “Previously Mitigated.” Previously mitigated or recurring vulnerabilities can be the result of systems not being restarted after a patch was applied, virtual systems reverting to previous snapshots, or services that were disabled or failed to restart. Organizations can use this component to focus efforts on remediating both current and previously mitigated vulnerabilities.
- SCCM Patch Management – SCCM Detected Vulnerabilities: This component provides a summary of Microsoft vulnerabilities detected by SCCM. Results from other patch management systems deployed on the network may also be included within the vulnerability results. Tenable supports a wide variety of patch management systems, which include SCCM, IBM BigFix, Symantec Altiris, and Dell KACE K1000. Each row is separated by severity level and includes vulnerabilities discovered within the Windows: Bulletin Plugin Family. Each column includes the total number of vulnerabilities discovered, number of vulnerabilities discovered by Nessus that SCCM is reporting as vulnerable, along with mitigated and exploitable vulnerabilities. Information presented within this component can be used to discover whether vulnerabilities are being patched by SCCM in a timely manner, along with hosts reporting outdated vulnerability information.
- SCCM Patch Management – Nessus Detected Vulnerabilities: This component provides a summary of Microsoft vulnerabilities detected by Nessus that have been reported as not vulnerable by SCCM. The rows are separated by severity level and includes vulnerabilities discovered within the Windows: Bulletin Plugin Family. Each column includes the total number of vulnerabilities discovered by SCCM, number of vulnerabilities discovered by Nessus that SCCM is reporting as not vulnerable, along with mitigated and exploitable vulnerabilities. Information presented within this component provides targeted information the analyst can use to identify how often systems are being patched by SCCM, and whether current security settings need to be modified.
- SCCM Patch Management – Unmanaged Vulnerabilities: This component provides a summary of vulnerabilities detected by Nessus on systems not managed by patch management systems. Each row is separated by severity level, and includes Microsoft vulnerabilities discovered within the Windows: Bulletin Plugin Family. Each column includes the total number of vulnerabilities discovered on unmanaged systems, along with mitigated, and exploitable vulnerabilities. This table provides targeted information analysts need to compare the effectiveness of SCCM patch management efforts, and whether current security settings need to be modified.
- SCCM Patch Management - Client Detection Per Class C: This chart presents a Class C summary of hosts managed by a SCCM server. Nessus actively scans the registry of each Windows host to determine whether hosts have SCCM clients installed. Enabling an enterprise-wide patch management solution such as SCCM, will aid the organization in protecting critical systems from compromise, and reducing overall risk. Organizations that have stand-alone or isolated hosts within the network should always be included in any patch management policy. Analysts can use this component to identify these types of hosts within the network that may not be fully patched or a part of a patch management solution.