by Stephanie Dunn
June 20, 2016
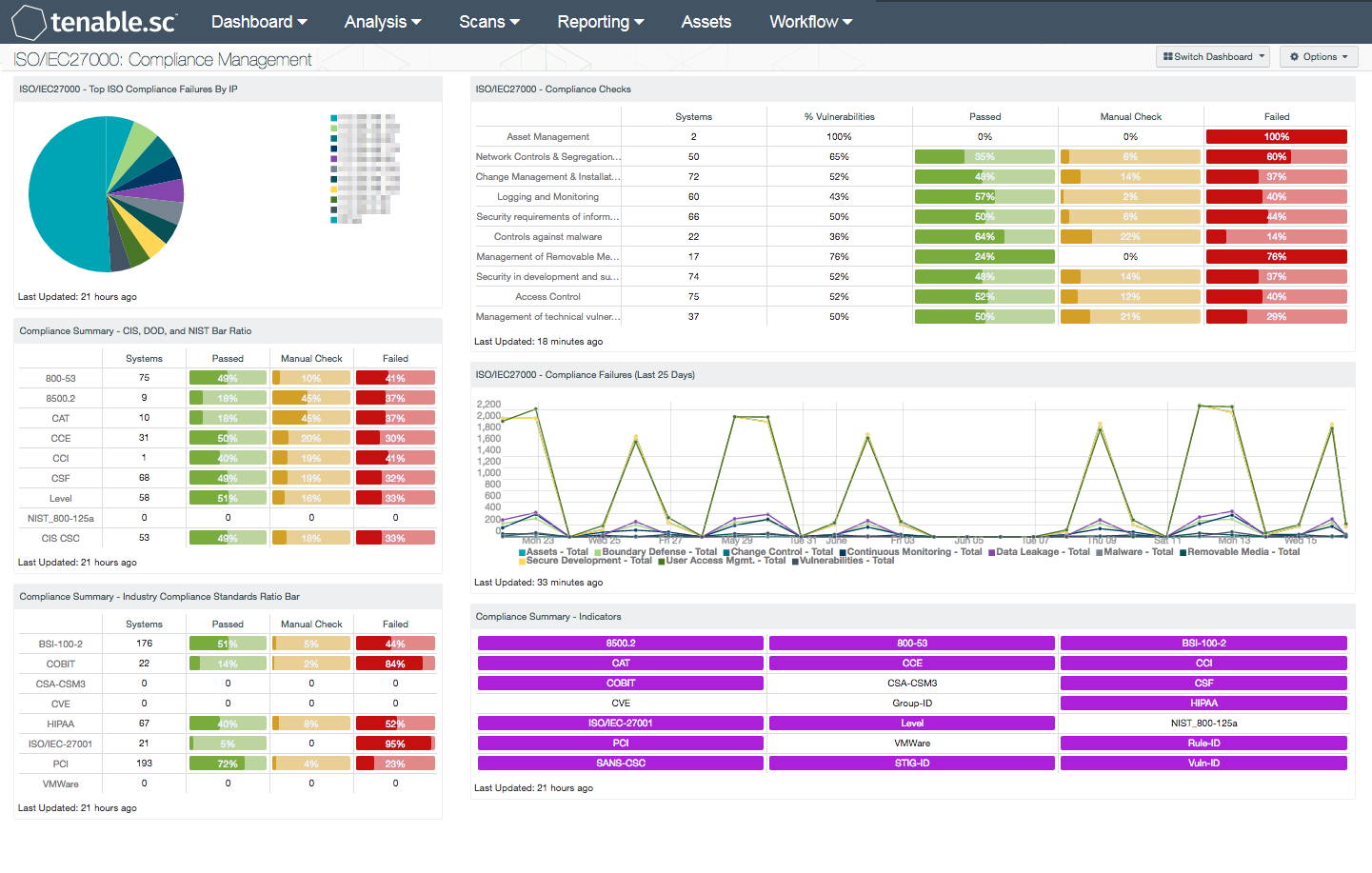
Organizations adopting compliance frameworks can face significant challenges in protecting network assets. Many organizations focus compliance efforts on manual tasks and short-term efforts that become unnecessary, and do not address the actual security risks faced by an organization. This Assurance Report Card (ARC) will provide a summary of systems with high-risk compliance issues, which can be used to address compliance risks in a timely manner.
Compliance frameworks comprise of specific guidelines that help organizations create or improve security management policies. Additionally, frameworks can provide an assessment of an organization’s current security risks, and best practices to achieve compliance. The ARC aligns with the compliance controls of the ISO/IEC 27002 framework, which will provide an accurate look into an organization’s current compliance status, and whether existing security controls are effective.
Every organization is responsible for protecting various types of confidential information, including customer data, Social Security numbers, credit card information, internal employee data, and more. In order to maintain compliance, organizations must first identify applicable threats and vulnerabilities. This will provide a structured approach that is tailored to the organization, and will allow security teams to proactively address and remediate compliance risks.
Policy statements included within this ARC will highlight compliance failures within the organization. Each policy statement includes specific compliance controls related to the series of ISO/IEC 27000 dashboards. Compliance failures can consist of misconfigured policies and device settings that are considered to be insecure. Security teams should review compliance failures to determine if the risks present are relevant to the organization. Policy statements can be customized as needed to meet organizational requirements. The ARC can help organizations prioritize and track compliance remediation efforts across the enterprise.
This ARC is available in the Tenable.sc Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, Assurance Report Cards, and assets. The ARC can be easily located in the Feed under the category Compliance. The ARC requirements are:
- Tenable.sc 5.3.2
- Nessus 8.5.1
- Compliance Data
- Local Checks
Tenable's Tenable.sc Continuous View (Tenable.sc CV) is the market-defining continuous network monitoring platform. Tenable.sc CV includes active vulnerability detection with Tenable Nessus and passive vulnerability detection with Tenable Nessus Network Monitor (NNM), as well as log correlation with Tenable Log Correlation Engine (LCE). Tenable.sc CV can help an organization continuously monitor and measure the effectiveness of security controls. Using Tenable.sc CV, an organization will obtain the most comprehensive and integrated view of its network security posture.
The following policy statements are included in this ARC:
Less than 5% of asset compliance checks failed: This policy statement displays the number of failed to total asset compliance checks. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. Asset compliance failures may indicate issues with misconfigured policies or device settings. Analysts should review all compliance check failures to determine the risk to the organization. Compliance is measured against those policy checks that reference one or more of the following standards:
- ISO 27001 A 8.1.1 (Identify organizational assets and define appropriate protection responsibilities)
- ISO 27001 A 8.1.2 (Assets maintained in the inventory should be owned)
- Cybersecurity Framework ID.AM-1 (Access permissions are managed, incorporating the principles of least privilege and separation of duties)
- Cybersecurity Framework ID.AM-2 (Access permissions are managed, incorporating the principles of least privilege and separation of duties)
Less than 5% of boundary defense compliance checks failed: This policy statement displays the number of failed to total boundary defense compliance checks. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. Boundary device compliance failures may indicate issues with services, configuration settings, and device policies. Analysts should review all compliance check failures to determine the risk to the organization. Compliance is measured against those policy checks that reference one or more of the following standards:
- ISO 27001 A13.1.1 (Networks should be managed and controlled to protect information in systems and applications)
- ISO 27001 A13.1.3 (Groups of information services, users, and information systems should be segregated on networks)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.AC-3 (Remote access is managed)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.AC-5 (Network integrity is protected, incorporating network segregation where appropriate)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.DS-2 (Data-in-transit is protected)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.PT-4 (Communications and control networks are protected)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.DS-5 (Protections against data leaks are implemented)
Less than 5% of change control compliance checks failed: This policy statement displays the number of failed to total change control compliance checks. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. Change control compliance failures may indicate device settings, file system issues, and unnecessary protocols or services that need to be disabled. Analysts should review all compliance check failures to determine the risk to the organization. Compliance is measured against those policy checks that reference one or more of the following standards:
- ISO 27001 A12.1.2 (Changes to the organization, business processes, information processing facilities, and systems that affect information security should be controlled)
- ISO 27001 A12.5.1 (Procedures should be implemented to control the installation of software on operational systems)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.IP-1 (A baseline configuration of information technology/industrial control systems is created and maintained)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.IP-3 (Configuration change control processes are in place)
- Cybersecurity Framework DE.CM-5 (Unauthorized mobile code is detected)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.DS-6 (Integrity checking mechanisms are used to verify software, firmware, and information integrity)
Less than 5% of continuous monitoring compliance checks failed: This policy statement displays the number of failed to total continuous monitoring compliance checks. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. Continuous monitoring compliance failures may indicate systems with logging and auditing setting issues. Analysts should review all compliance check failures to determine the risk to the organization. Compliance is measured against those policy checks that reference one or more of the following standards:
- ISO 27001 A12.4 (To record events and generate evidence)
- Cybersecurity Framework DE.CM-3 (Personnel activity is monitored to detect potential cybersecurity events)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.PT-1 (Audit/log records are determined, documented, implemented, and reviewed in accordance with policy)
- Cybersecurity Framework RS.AN-1 (Notifications from detection systems are investigated)
Less than 5% of data leakage compliance checks failed: This policy statement displays the number of failed to total data leakage compliance checks. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. Data leakage compliance failures may indicate systems with registry settings, permission, and ownership issues. Analysts should review all compliance check failures to determine the risk to the organization. Compliance is measured against those policy checks that reference one or more of the following standards:
- ISO 27001 A14.1 (Ensure that information security is an integral part of information systems across the entire lifecycle)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.IP-2 (A System Development Life Cycle to manage systems is implemented)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.DS-2 (Data-in-transit is protected)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.DS-5 (Protections against data leaks are implemented)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.DS-6 (Integrity checking mechanisms are used to verify software, firmware, and information integrity)
Less than 5% of malware compliance checks failed: This policy statement displays the number of failed to total malware compliance checks. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. Malware compliance failures may indicate issues with IDS/IPS device settings, or anti-virus system policies. Analysts should review all compliance check failures to determine the risk to the organization. Compliance is measured against those policy checks that reference one or more of the following standards:
- ISO 27001 A12.2.1 (Detection, prevention, and recovery controls to protect against malware should be implemented, combined with appropriate user awareness)
- Cybersecurity Framework DE.CM-4 (Malicious code is detected)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.DS-6 (Integrity checking mechanisms are used to verify software, firmware, and information integrity)
- Cybersecurity Framework RS.MI-2 (Incidents are mitigated)
Less than 5% of removable media compliance checks failed: This policy statement displays the number of failed to total removable media compliance checks. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. Removable media compliance check failures may indicate issues with file, group, or auditing practices. Analysts should review all compliance check failures to determine the risk to the organization. Compliance is measured against those policy checks that reference one or more of the following standards:
- ISO 27001 A8.3.1 (Procedures should be implemented for the management of removable media in accordance with the classification scheme adopted by the organization)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.DS-3 (Assets are formally managed throughout removal, transfers, and disposition)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.IP-6 (Data is destroyed according to policy)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.PT-2 (Removable media is protected and its use restricted according to policy)
Less than 5% of secure development compliance checks failed: This policy statement displays the number of failed to total secure development compliance checks. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. Secure development compliance configuration failures may indicate insecure database configurations, group policies settings, and Windows registry changes. Analysts should review all compliance check failures to determine the risk to the organization. Compliance is measured against those policy checks that reference one or more of the following standards:
- ISO 27001 A14.2 (To ensure that information security is designed and implemented within the development lifecycle of information systems)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.IP-1 (A baseline configuration of information technology/industrial control systems is created and maintained)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.IP-2 (A System Development Life Cycle to manage systems is implemented)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.IP-3 (Configuration change control processes are in place)
- Cybersecurity Framework DE.CM-6 (External service provider activity is monitored to detect potential cybersecurity events)
- Cybersecurity Framework DE.DP-3 (Detection processes are tested)
Less than 5% of user access compliance checks failed: This policy statement displays the number of failed to total user access compliance checks. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. User access compliance checks failures may indicate issues with user and/or group settings. Analysts should review all compliance check failures to determine the risk to the organization. Compliance is measured against those policy checks that reference one or more of the following standards:
- ISO 27001 A.9.1 (To limit access to information and information processing facilities)
- ISO 27001 A.9.2 (To ensure authorized user access and to prevent unauthorized access to systems and services)
- ISO 27001 A.9.3 (To make users accountable for safeguarding their authentication information)
- ISO 27001 A.9.4 (To prevent unauthorized access to systems and applications)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.AC-1 (Identities and credentials are managed for authorized devices and users)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.AC-4 (Access permissions are managed, incorporating the principles of least privilege and separation of duties)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.DS-5 (Protections against data leaks are implemented)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.PT-3 (Access to systems and assets is controlled, incorporating the principle of least functionality)
Less than 5% of vulnerabilities compliance checks failed: This policy statement displays the number of failed to total vulnerability compliance checks. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. Vulnerability compliance failures may indicate issues with device settings, user permissions, and group policies. Analysts should review all compliance check failures to determine the risk to the organization. Compliance is measured against those policy checks that reference one or more of the following standards:
- ISO 27001 A.12.6.1 (Information about technical vulnerabilities of information systems being used should be obtained in a timely fashion, the organization’s exposure to such vulnerabilities evaluated and appropriate measures taken to address the associated risk)
- Cybersecurity Framework DE.CM-8 (Vulnerability scans are performed)
- Cybersecurity Framework ID.RA-1 (Asset vulnerabilities are identified and documented)
- Cybersecurity Framework ID.RA-5 (Threats, vulnerabilities, likelihoods, and impacts are used to determine risk)
- Cybersecurity Framework PR.IP-12 (A vulnerability management plan is developed and implemented)
- Cybersecurity Framework RS.MI-3 (Newly identified vulnerabilities are mitigated or documented as accepted risks)