by David Schwalenberg
October 10, 2016
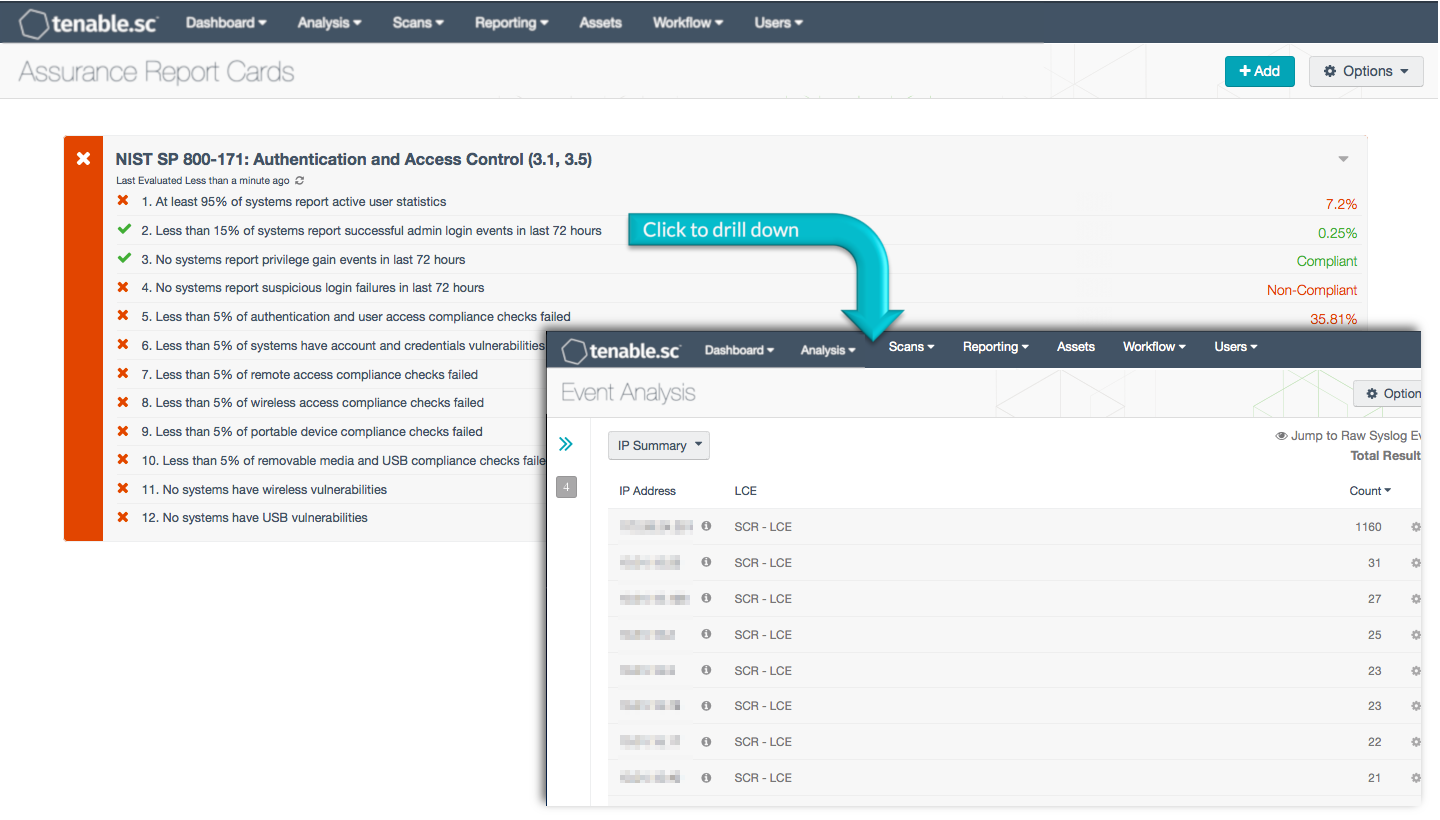
Organizations rely on robust authentication, access control, and enforcement of least privilege to protect critical systems and sensitive data. Without proper user authentication and account management, an organization may not know who has access to their network, whether or not the old accounts of former employees are still active, and whether or not user passwords meet policy requirements. Default credentials that have not been changed and are well known to attackers could allow systems to be exploited and data to be lost. Without enforcement of least privilege, users on the organization's network may inadvertently access systems or information they should not access, change files, or install malware on the network. Without proper access control, intruders may gain access to the organization's network and sensitive data through compromised mobile devices or removable media, or through remote or wireless means.
The federal government relies heavily on external service providers and contractors to assist in carrying out a wide range of federal missions. Sensitive but unclassified federal information is routinely processed by, stored on, or transmitted through nonfederal information systems. Failing to properly protect this Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) could impact the ability of the federal government to successfully carry out required missions and functions.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) created Special Publication 800-171 "Protecting Controlled Unclassified Information in Nonfederal Information Systems and Organizations" to provide recommended requirements for protecting the confidentiality of CUI. Federal agencies should use these requirements when establishing contracts and agreements with nonfederal entities that process, store, or transmit CUI.
This Assurance Report Card (ARC) aligns with the Access Control (section 3.1) and Identification and Authentication (section 3.5) families of security requirements in NIST SP 800-171. These families are closely related and focus on limiting access to CUI through control of information system access and strong user authentication. Using this ARC, an organization will be better able to monitor authentication and access control. This information will assist the organization in managing and properly restricting access to information systems that process, store, or transmit CUI.
More details on each of the policy statements included in the ARC are given below. Clicking on a policy statement will bring up the analysis screen to display more details related to that policy statement. The ARC policy statement parameters are guides that can be customized as necessary to meet organizational requirements.
This ARC is available in the Tenable.sc Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, Assurance Report Cards, and assets. The ARC can be easily located in the Tenable.sc Feed under the category Compliance. The ARC requirements are:
- Tenable.sc 5.4.0
- Nessus 8.4.0
- LCE 6.0.0
- NNM 5.9.0
- Compliance data
Tenable's Tenable.sc Continuous View (CV) is the market-defining continuous network monitoring solution, and can assist an organization in securing and controlling access. Tenable.sc CV is continuously updated with information about advanced threats, zero-day vulnerabilities, and new regulatory compliance data. Active scanning periodically examines systems to find account and credentials vulnerabilities and enumerate system information. Audit files can be used to assess compliance with authentication policies. Passive listening provides real-time monitoring to collect information about systems and vulnerabilities. Host data and data from other security investments is analyzed to monitor user activity across the network. Tenable.sc CV provides an organization with the most comprehensive view of the network and the intelligence needed to secure user authentication, control access, and safeguard sensitive information.
ARC Policy Statements
At least 95% of systems report active user statistics: This policy statement displays the percentage of total systems that report user statistics. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. The Tenable Log Correlation Engine (LCE) can gather user statistics from systems on a network. All systems should be reporting user statistics to LCE to ensure that access controls can be effectively implemented and monitored.
Less than 15% of systems report successful admin login events in last 72 hours: This policy statement displays the percentage of systems from which LCE collected logs that have had successful administrative user login events in the last 72 hours. Clicking on the policy statement to bring up the analysis screen and setting the tool to User Summary will display the user accounts that logged in administratively. Any unexpected users in this list should be further investigated to determine why and how they are executing administrative actions.
No systems report privilege gain events in last 72 hours: This policy statement displays non-compliant if any systems from which LCE collected logs have had privilege gain events in the last 72 hours. These privilege gain events may indicate an attack or intrusion. Systems on which privilege gains are occurring should be further investigated to ensure that they are not compromised.
No systems report suspicious login failures in last 72 hours: This policy statement displays non-compliant if any systems from which LCE collected logs have had suspicious login failure events in the last 72 hours. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. Suspicious failed logins may include attempts to log in with default or invalid user accounts and repeated login failures, among other things. These suspicious events should be investigated to determine if any malicious behavior is occurring.
Less than 5% of authentication and user access compliance checks failed: This policy statement displays the percentage of user access compliance checks that failed. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. User access settings may include password requirements and requirements to disable services, among other things. Compliance is measured against those policy checks that reference standards such as the Cybersecurity Framework, NIST 800-53, NIST 800-171, the CIS Critical Security Controls, and ISO/IEC 27001.
Less than 5% of systems have account and credentials vulnerabilities: This policy statement displays the percentage of total systems that have account and credentials vulnerabilities. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. Account and credentials vulnerabilities may include default or blank password detections and weak authentication, among other things. Account and credentials vulnerabilities should be remediated in order to protect systems and prevent valuable data from being stolen.
Less than 5% of remote access compliance checks failed: This policy statement displays the percentage of remote access compliance checks that failed. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. Remote access settings may include requirements to disable certain remote access services and set appropriate permissions, among other things. To protect systems against unauthorized access, remote access compliance issues must be addressed.
Less than 5% of wireless access compliance checks failed: This policy statement displays the percentage of wireless compliance checks that failed. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. Wireless settings may include requirements to deactivate wireless interfaces and set specific configurations, among other things. To improve wireless security and protect against unauthorized access, wireless compliance issues must be addressed.
Less than 5% of portable device compliance checks failed: This policy statement displays the percentage of portable device compliance checks that failed. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. Portable device settings may include requirements to install personal firewalls and use encryption on mobile devices, among other things. To protect against data loss or system compromise, removable media compliance issues must be addressed.
Less than 5% of removable media and USB compliance checks failed: This policy statement displays the percentage of removable media and USB compliance checks that failed. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. Removable media and USB settings may include requirements to turn off Autoplay and disable USB, among other things. To protect against data loss or system compromise, removable media compliance issues must be addressed.
No systems have wireless vulnerabilities: This policy statement displays non-compliant if any systems have wireless vulnerabilities. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. Wireless vulnerabilities can leave the network exposed to malicious activity and need to be remediated.
No systems have USB vulnerabilities: This policy statement displays non-compliant if any systems have USB vulnerabilities. If the policy statement requirement is met, the result is displayed in green; otherwise, the result is displayed in red. USB vulnerabilities can leave the network exposed to malicious activity and need to be remediated.